Numerical study of conduction heat transfer from toroidal shaped surfaces into an infinite domain
Abstract
The mathematical formulation for steady conduction heat transfer from a toroidal geometry into an infinite medium is presented. The torus is in thermal communication with the infinite medium through a heat transfer coefficient at the torus' external surface. The mathematical formulation is presented using the Toroidal coordinate system; a finite element grid is developed usign this coordinate system as the basis for development. Mesh refinement studies indicate convergence of the numerical solutions to a very high accuracy. Results are presented in tabular and graphic form for diameter ratios ranging from 1.1 to 10 and for the Biot modulus ranging from 0.01 through to 10 exp 20.
Being discharged. In a charging process, heat transfer from the hot gas increases thermal energy stored within the colder spheres; during discharge, the stored energy decreases as heat is transferred from the warmer 321 An experiment has been performed under conditions for which the wafer, initially at a uniform temperature. Buy Conduction heat transfer by Paul J. Schneider online at Alibris. We have new and used copies available, in 1 editions - starting at $8.38. Conduction A mode of heat transfer in which heat energy is transferred within an object itself or between objects in contact. When a cold spoon is left in a pot of boiling water, the spoon eventually becomes hot. This is an example of conduction. Conduction is one of the three forms of heat transfer, which also include Convection and Radiation. Conduction Heat Transfer by Schneider, P J and a great selection of related books, art and collectibles available now at AbeBooks.co.uk.
Conduction Heat Transfer Examples

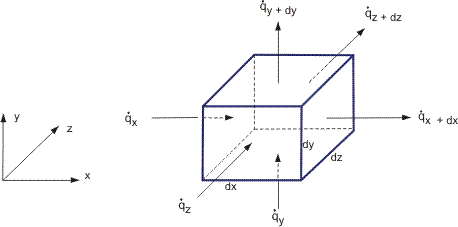
Conduction Heat Transfer Equation
- Conductive Heat Transfer;
- Coordinates;
- Toroids;
- Computational Grids;
- Finite Element Method;
- Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer